Newer Version of A* Search
Note: Also see a text explanation of
A* search
and the pseudo code version
of the algorithm.
;;; ASTAR2000.LSP - Updated version
;;; A* Search for a shortest path.
;;; (C) Copyright 1995 by Steven L. Tanimoto.
;;; This program is described in Chapter 5 ("Search") of
;;; "The Elements of Artificial Intelligence Using Common Lisp," 2nd ed.,
;;; published by W. H. Freeman, 41 Madison Ave., New York, NY 10010.
;;; Permission is granted for noncommercial use and modification of
;;; this program, provided that this copyright notice is retained
;;; and followed by a notice of any modifications made to the program.
;;; Here is the representation of the adjacency distance data,
;;; plus functions for getting at it and at solution path info.
;;; This code is identical to that in UNIFCOST.CL
(let ((distance-info (make-hash-table :size 20))
(path-predecessor-info (make-hash-table :size 20)) )
(defun set-distances (x y)
(setf (gethash x distance-info) y) )
(defun get-distances (x)
(gethash x distance-info) )
(defun set-predecessor (x y)
(setf (gethash x path-predecessor-info) y) )
(defun get-predecessor (x)
(gethash x path-predecessor-info) )
)
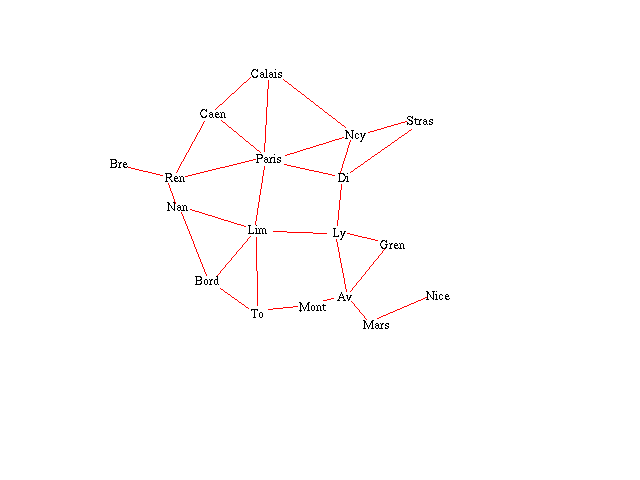
;;; Here are actual inter-city distances from the Michelin map:
(set-distances 'brest '((rennes . 244)))
(set-distances 'rennes '((caen . 176)(paris . 348)
(brest . 244)(nantes . 107)))
(set-distances 'caen '((calais . 120)(paris . 241)(rennes . 176)))
(set-distances 'calais '((nancy . 534)(paris . 297)(caen . 120)))
(set-distances 'nancy '((strasbourg . 145)(dijon . 201)
(paris . 372)(calais . 534)))
(set-distances 'strasbourg '((dijon . 335)(nancy . 145)))
(set-distances 'dijon '((strasbourg . 335)(lyon . 192)
(paris . 313)(nancy . 201)))
(set-distances 'lyon '((grenoble . 104)(avignon . 216)
(limoges . 389)(dijon . 192)))
(set-distances 'grenoble '((avignon . 227)(lyon . 104)))
(set-distances 'avignon '((grenoble . 227)(marseille . 99)
(montpellier . 121)(lyon . 216)))
(set-distances 'marseille '((nice . 188)(avignon . 99)))
(set-distances 'nice '((marseille . 188)))
(set-distances 'montpellier '((avignon . 121)(toulouse . 240)))
(set-distances 'toulouse '((montpellier . 240)(bordeaux . 253)
(limoges . 313)))
(set-distances 'bordeaux '((limoges . 220)(toulouse . 253)
(nantes . 329)))
(set-distances 'limoges '((lyon . 389)(toulouse . 313)
(bordeaux . 220)(nantes . 329)(paris . 396)))
(set-distances 'nantes '((limoges . 329)(bordeaux . 329)
(rennes . 107)))
(set-distances 'paris '((calais . 297)(nancy . 372)(dijon . 313)
(limoges . 396)(rennes . 348)(caen . 241)))
;;; And here is the hash table F-VALUES to
;;; remember the heuristic value at each node visited.
;;; We also need a hash table for G-VALUES.
(let ((f-values (make-hash-table :size 20))
(g-values (make-hash-table :size 20)) )
(defun set-f-value (x y)
(setf (gethash x f-values) y) )
(defun get-f-value (x)
(gethash x f-values) )
(defun set-g-value (x y)
(setf (gethash x g-values) y) )
(defun get-g-value (x)
(gethash x g-values) )
)
;;; Next is the information about longitude, which is the same
;;; as that used in BESTFS2.CL
(let ((longitude-info (make-hash-table :size 20)))
(defun set-longitude (x y)
(setf (gethash x longitude-info) y) )
(defun get-longitude (x)
(gethash x longitude-info) )
)
;;; The longitude of each city is stored in tenths of a degree.
;;; We again use a local function with a LAMBDA form, since
;;; SET-LONGITUDE takes two arguments but we want a
;;; function that takes one argument for this use with MAPCAR.
(mapcar #'(lambda (pair) (apply #'set-longitude pair))
'((avignon 48)(bordeaux -6)(brest -45)(caen -4)
(calais 18)(dijon 51)(grenoble 57)(limoges 12)
(lyon 48)(marseille 53)(montpellier 36)
(nantes -16)(nancy 62)(nice 73)(paris 23)
(rennes -17)(strasbourg 77)(toulouse 14) ) )
;;; Now we are ready for the algorithm itself.
;;; A-STAR-SEARCH is the main searching procedure.
(defun a-star-search (start-node goal-node)
"Performs a search with the A* algorithm."
(set-goal goal-node)
(let ((open (list start-node)) ;step1
(closed nil)
x
successors)
(set-predecessor start-node nil)
(set-g-value start-node 0)
(set-f-value start-node (f start-node))
(loop
(if (null open)(return 'failure)) ;step2
(setf x (select-best open)) ;step3
(setf open (remove x open)) ;step4
(push x closed)
(if (eql x (get-goal))
(return (extract-path x)) ) ;step5
(setf successors (get-successors x)) ;step6
(dolist (y successors) ;step7
(if (not (or (member y open)
(member y closed) ))
(progn
(increment-count)
(set-g-value y (g y x))
(set-f-value y (f y))
(setf open (insert y open))
(set-predecessor y x) ;; y is not in open or closed
;; For Tracing:
;; Use a trace "format" statement here for
;; values of Y not on open or closed
;; Print the value of Y, X, Open, Closed,
;; f(y)=g(y)+h(y) and f(x)=g(x)+y(x) - for g use get-g-value
;; Also print the successors of X.
) ;;end of progn
(let* ((z (get-predecessor y)) ;; y is in open or closed
(temp (if z
(+ (- (get-f-value y)
(get-g-value z)
(arc-dist z y) )
(get-g-value x)
(arc-dist x y) )
(get-f-value y) ) ) )
(if (< temp (get-f-value y))
(progn
;; For Tracing:
;; Use a trace "format" statement here for Y when Y is in open or
;; closed. Print values for:
;; open, closed, Y, Z, X, temp
;; f(y)=g(y)+h(y), f(z)=g(z)+h(z), f(x)=g(x)+h(x)
;; Also use a format to print the values of:
;; distance to Y through Z (this is the current f of Y)
;; and the distance to Y through X (this is temp)
(set-g-value y
(+ (- (get-g-value y)
(get-f-value y) )
temp) )
(set-f-value y temp)
(set-predecessor y x)
(if (member y open)
(progn
(setf open (remove y open))
(setf open (insert y open)) ) )
(if (member y closed)
(progn
(setf open (insert y open))
(setf closed
(remove y closed) )
)
)
) ;;end of prog
) ;; end of if
;; For Tracing:
;; At the end of the dolist loop (for Y's not in open/closed), print:
;; X, Y, f(y)=g(y)+h(y) f(x)=g(x)+h(x)
;; and print the successors of X
) ;; end of let
) ;; end of dolist
) ;; end of loop
; end of loop -------- this is implicitly step8
) ) )
;; The supporting functions:
;;; Use local variable to keep track of the goal.
(let (goal)
(defun set-goal (the-goal) (setf goal the-goal))
(defun get-goal () goal) )
;;; F is the sum of G and H.
(defun f (n)
"Computes F value for node N."
(+ (get-g-value n) (h n)) )
;;; G computes the distance from the start node to NODE
;;; by adding the distance from X to NODE to X's distance.
(defun g (node x)
"Returns distance from START-NODE to NODE"
(+ (get-g-value x) (arc-dist x node)) )
;;; H evaluates the difference in longitude between
;;; the current node N and the goal node.
(defun h (n)
"Returns an estimate of the distance from N
to the goal."
(* 10 (longitude-diff n (get-goal))) )
;;; LONGITUDE-DIFF returns the absolute value of the
;;; difference in longitudes between nodes N1 and N2
;;; in tenths of a degree.
(defun longitude-diff (n1 n2)
"Computes difference in longitudes."
(abs (- (get-longitude n1) (get-longitude n2))) )
;;; SELECT-BEST chooses a node in step 3...
(defun select-best (lst)
"Returns the best node on LST for expansion."
(if (eql (first lst) (get-goal))
(first lst)
(better (first lst)(rest lst)) ) )
;;; The helping function BETTER for SELECT-BEST checks
;;; to see if there is a goal node on LST with FVALUE
;;; as low as that of ELT. If so, it returns the goal node.
;;; If not, it returns ELT.
(defun better (elt lst)
"Returns a goal-node on LST if it has an equal value,
otherwise ELT."
(cond ((null lst) elt)
((< (get-f-value elt)(get-f-value (first lst)))
elt)
((eql (first lst) (get-goal))
(first lst) )
(t (better elt (rest lst))) ) )
;;; INSERT puts NODE onto LST, which is ordered
;;; by FVALUE.
(defun insert (node lst)
"Inserts NODE onto LST, according to FVALUE ordering."
(cond ((null lst)(list node))
((< (get-f-value node)
(get-f-value (first lst)) )
(cons node lst) )
(t (cons (first lst)
(insert node (rest lst)) )) ) )
;;; EXTRACT-PATH returns the sequence of cities found.
(defun extract-path (n)
"Returns the path from START-NODE to N."
(cond ((null n) nil)
(t (append (extract-path (get-predecessor n))
(list n) )) ) )
;;; GET-SUCCESSORS retrieves the list of cities adjacent
;;; to N from the hash table.
(defun get-successors (n)
"Returns a list of cities adjacent to N."
(mapcar #'first (get-distances n)) )
;;; Let BIG-DISTANCE represent an impossibly large distance
;;; for this problem:
(defconstant big-distance 9999)
;;; ARC-DIST retrieves the distance between N1 and N2.
(defun arc-dist (n1 n2)
"Returns the distance along arc N1 N2. If no such arc
exists, returns BIG-DISTANCE."
(or (rest (assoc n1 (get-distances n2))) big-distance) )
;;; Use a local variable EXPANSION-COUNT for counting the
;;; number of nodes expanded by the algorithm.
(let (expansion-count)
(defun initialize-count () (setf expansion-count 0))
(defun increment-count () (incf expansion-count))
(defun get-count () expansion-count) )
;;; TEST sets EXPANSION-COUNT to 0 and
;;; begins a search from RENNES to AVIGNON.
(defun test ()
"Runs a test of ASTAR."
(initialize-count)
(format t "A-star-search solution: ~s.~%"
(a-star-search 'rennes 'avignon) )
(format t "Path-length: ~s.~%"
(get-f-value 'avignon) )
(format t "~s nodes expanded.~%"
(get-count) )
)
;; Uncomment the following line if you want the test function
;; to run automatically when the program is loaded:
;; (test)