AI Fall 2009
- Course webpage
- Syllabus
- Python.org,
Python tutorial (Guido van Rossum),
Beginner's Guide,
more documentation from the Python site
- Unit 1 Word ladders
- Three letter words dictionary to demo depth first and breadth first
Three letter words with a loop
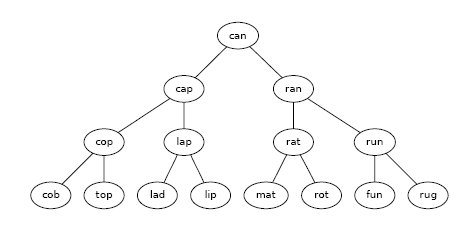
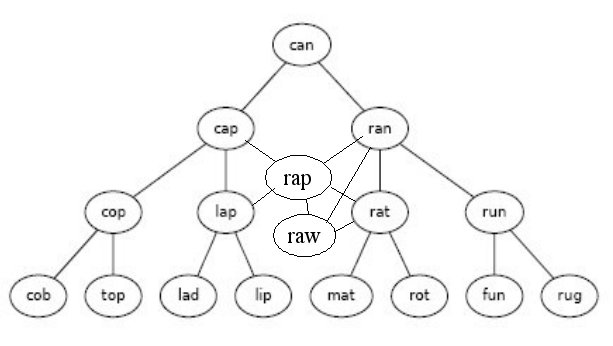
- Preliminary program steps for Lab 1 - construct a "word ladder" consisting of all the words 1 letter different from a given word:
- Assignment for Lab 1:
- Assignment (.doc)
- Write functions read_words, countDiff, printLadder, main
- Complete the pdf
Lab 1
- words.txt and
wordsShort.txt - many of these alternate versions use this shortened word dictionary
- spell.py programs from the our website
- spell_0.py, sample
output
understand what this syntax is doing: wlist=open('words.txt').read().split('\n')[:-1]
Or alternate spell_0.py with traditional syntax
- spell_1.py
understand the syntax for reading from a file, and how to use a for loop in Python
- spell_1B.py
how to use a while loop that stops when an item is found, using a boolean variable
Or alternate spell_1.py with alternate syntax reading the file line by line, adding each new word into the wordlist.
- spell_2.py
defining a function in Python, using break to exit a while loop. Print the position in the dictionary of the located word
Or alternate spell_2.py with boolean variable "found"
- spell_3.py
Using a while-else loop,
more about while-else
- spell_4.py
- Steps to take in solving Lab01, the neighbors lab
- nbrs00.out
Using a shortened dictionary file, keep asking for more words to try until *quit* is entered
- nbrs_0Prelim1.out
Enter a second string to match a given word, for example "abated". Count the number of characters different.
- nbrs_0Prelim2.out
Enter a word, go through the entire short dictionary and count the characters different for each other word.
- nbrs_0Prelim3.out
Enter a second string to match a given word, for example "abated". Count the number of characters different. Print "NEIGHBOR" each time a neighbor is found. Add each NEIGHBOR to a neighborlist. Print this final neighborlist.
- nbrs.out
Enter words from the dictionary, print the neighborlist for each.
- freq.py programs:
- freq_0.py: study Python "zip" function, used to construct a list of tuples for each character in a string
lowercase="abcdefg"
ziplist=zip(lowercase,[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]) # or zip(lowercase,[0]*10)
# ziplist <- [('a', 0), ('b', 0), ('c', 0), ('d', 0), ('e', 0), ('f', 0), ('g', 0), ('h', 0), ('i', 0), ('j', 0)]
dictionary=dict(ziplist) # construct a "dictionary" or "hash table"
# dictionary <- {'a': 0, 'c': 0, 'b': 0, 'e': 0, 'd': 0, 'g': 0, 'f': 0, 'i': 0, 'h': 0, 'j': 0}
- Or alternate freq_0.py version with traditional syntax, not using "zip" and "dict" functions, using more traditional syntax for file reading and constructing the dictionary
- Alternate freq_1.py with traditional syntax
- Preliminary program steps for Lab 2 - constructing a word ladder of 6-letter words (each new word changes by one letter) in which the first and last word differ by 6
- Lab 2 step 1 - Choose a random word from the list, make a list of all the words in the word list that are 1 letter different from the original word
- Lab 2 step 2 - Choose a random word from the list. Make a list of neighbors that consist of the words in wordlist that are 1 letter different from the previous word in this list. This version iterates through this process 5 times, each iteration finding a word 1 letter different from the current word.
- Lab 2 step 3 Choose a random word from the wordlist. Make a list of neighbors that consist of the words in wordlist that are 1 letter different from the previous word in the ladder. Continue this process extending the neighborlist through different words and their corresponding nbr lists. Continue until either:
- You reach a DEAD END with no new words to extend
- The length of the current neighbor list becomes greater than a certain amount, such as length 20
- The difference between the first and last words in the neighborlist is 6
- Assignment (.doc) for Lab 02
- Lab 2 writeup (pdf) - constructing a word ladder of 6-letter words (each new word changes by one letter) in which the first and last word differ by 6
Lisp programming and
sample tutorial

